
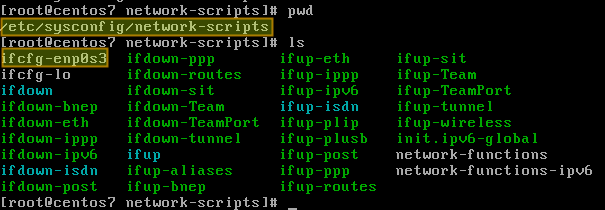
Run systemctl restart NetworkManager for changes to take effect. The end result will look like this: HWADDR=7C:67:2A:CF:EF:9F ESSID=Comtrend7FB9 MODE=Managed KEY_MGMT=WPA-PSK SECURITYMODE=open MAC_ADDRESS_RANDOMIZATION=default TYPE=Wireless IPADDR=192.168.0.22 PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=static DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=Comtrend7FB9 UUID=2f5a6217-37c7-449f-bfaa-1d3fa5283482 ONBOOT=yes In addition, the IP address used must be added to the file. The "BOOTPROTO = dhcp" boot protocol line needs to be changed to "BOOTPROTO = static". In this example, the file is called ifcfg-Comtrend7BF9 ( ifcfg- followed by the name of the connection). To change the network interface from dynamic to static, you need to edit the file in the / etc / sysconfig / network-scripts directory, representing the common interface. $ nmcli dev status DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION wlo1 wifi connected Comtrend7FB9 virbr0 bridge connected virbr0 enp3s0 ethernet unavailable - lo loopback unmanaged - virbr0-nic tun unmanaged. Note that the device name and connection name are not the same. The nmcli command shown below will list the network connections and devices on the system. To configure a static IP address on a Red Hat system, start by listing the connection of Network Manager. The best way is to look at the configuration file. But even dynamic addresses may not change. If the IP address on the Linux system changes when the system restarts, this is obviously a dynamic address. There is no simple command to determine if the IP address on a Linux system is assigned by DHCP or a static address.
Centos 7 static ip address how to#
Today's article will look at how to manage this task on both Red Hat systems (RHEL) and Ubuntu.
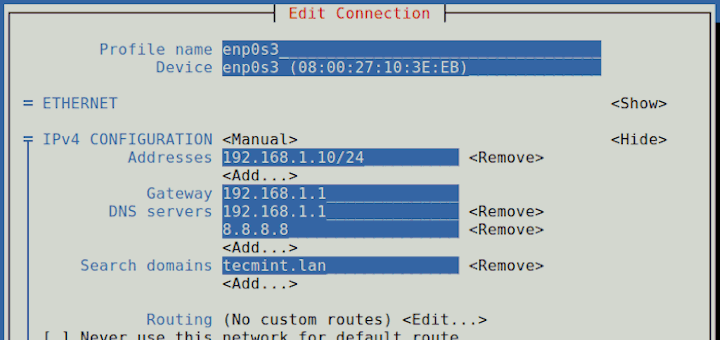
However, the process will vary slightly depending on the distribution you are using. Static IP addresses provide a consistent and consistent connection for users and applications.įortunately, the steps needed to change the Linux system IP address from dynamic to static are quite easy. However, when a system acts as a server or is managed remotely, it is more convenient to have a static address. They are called "dynamic addresses" and can be changed whenever the system is restarted. IP addresses on Linux systems are usually automatically assigned by the server Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Follow these steps to make the conversion. Here is the IP address of your Ubuntu desktop system.When you need a Linux system with a static IP address instead of a dynamically set address by DHCP, all you need to do is make some configuration changes and reboot the system. After that click icon to open setting for your systems network interface as shown in the below screen. In the left sidebar click on the Network tab.
Centos 7 static ip address windows#
Now, login to your CentOS Desktop system and open settings windows on your machine as showing in the below screen.
ip addr showįor this option, you must have Desktop installed on your CentOS 8 system. Now type following IP command to view current IP addresses configured on your system. Open a command terminal by pressing CTRL + ALT + T on your CentOS system. Method 1 – Check IP via Command (CentOS 8) You can either use the command prompt to check the current IP address on your system or use a GUI option to view the local IP address on your system.įollow this tutorial to configure new IP on CentOS 8 desktop system. The desktop provides an attractive GUI for working with it. Question – How to find the local IP address of CentOS 8 Linux system? 2 Ways to find IP address on CentOS 8Desktop edition or CentOS 8 Server edition?ĬentOS 8 is the latest available Linux operating system from the CentOS team.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
